Technology born for energy storage-flow battery
Technology born for energy storage-flow battery
In 1974, with funding from NASA, Thaller proposed a new type of electrochemical energy storage technology - flow battery.
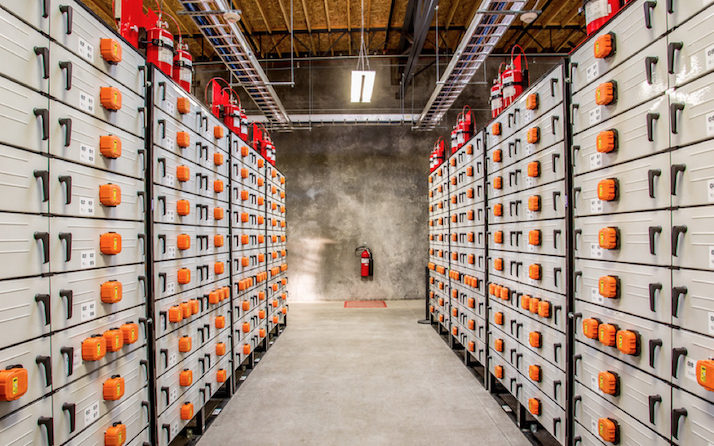
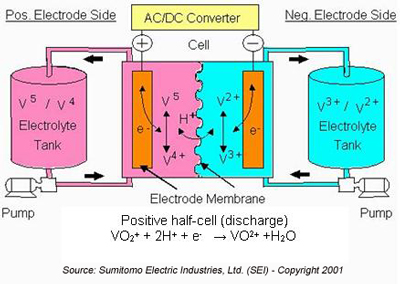
A flow battery is a high-performance battery that uses positive and negative electrolytes to separate and circulate separately. It has the characteristics of high capacity, wide application area and long cycle life. It is a new energy product.
After years of development, flow batteries have derived various routes such as all-vanadium flow batteries, zinc-bromine flow batteries, and iron-nickel flow batteries. At this stage, the all-vanadium route is the most mature and is the main route in my country. It has reached the early stage of commercialization. European and American countries are subject to the availability of vanadium, so they take the zinc-bromine route.
All-vanadium redox flow battery is a kind of battery with the same advantages and disadvantages. It is not difficult to find through detailed comparison that all-vanadium redox flow battery is the most suitable energy storage device, and it is not too much to say that it is born for energy storage.
Specifically, the all-vanadium flow battery has a high cycle number of 5,000-10,000 times, which means that the battery life may be as long as 20 years; it is not easy to burn, has good safety, and can discharge 100% without damaging the battery.
At the same time, the all-vanadium redox flow battery has a modular function. The power of the energy storage system can be controlled by increasing or decreasing the number of batteries, and the energy storage capacity can be adjusted by the volume and concentration of the electrolyte, which can meet the individualization of the energy storage end. Require.
These advantages are not available in other battery routes.
Of course, the all-vanadium redox flow battery is not perfect. Since the energy density is only 15-50Wh/kg, coupled with the liquid flow system, the volume of the all-vanadium redox flow battery is much larger than other batteries, and it is often used in containers or even buildings. way to store, not easy to move easily. At the same time, the all-vanadium redox flow battery also needs a relatively mild temperature environment, and the working temperature of 5-40 ° can be applied to not many scenarios.
These shortcomings affect the application of all-vanadium redox flow batteries in electric vehicles, but they are in line with the needs of energy storage stations, especially many large-scale energy storage stations, which require safe and stable energy storage equipment, which is undoubtedly stable and has a long life. The all-vanadium flow battery will be the first choice.
In terms of other batteries, lead-carbon batteries are not environmentally friendly, lithium batteries have potential safety hazards, zinc-bromine flow batteries have a strong self-discharge phenomenon, and sodium-sulfur batteries have high operating temperatures, which obviously do not match the requirements of energy storage stations.
Considering performance only, all-vanadium redox flow batteries are the best choice for energy storage scenarios.
The factor restricting the development of all-vanadium redox flow batteries is still the high cost, especially when the energy storage station can use second-hand electric vehicle power batteries in a cascade, which amplifies the disadvantages of the high cost of all-vanadium redox flow batteries.
According to incomplete statistics, the current cost of an all-vanadium flow battery is about 3-3.2 yuan/Wh, while the average cost of a lithium battery may only be 1.2-1.5 yuan/Wh, which is about 40% of that of an all-vanadium flow battery. .
Although the current cost of all-vanadium redox flow batteries is relatively high, compared with the historical trend of lithium battery prices, the cost of all-vanadium redox flow batteries is likely to drop sharply with scale.
In 1991, when lithium batteries were just commercialized, the cost of lithium batteries was as high as $7,523/KW, but with the continuous iteration and maturity of lithium battery technology, the price of lithium batteries fell all the way.
At present, the all-vanadium redox flow battery is in the early stage of the outbreak. The installed capacity in 2019 is 20MW, and the installed capacity in 2020 will reach 100MW. The growth rate is very fast but the absolute value is extremely low.
In terms of market share, the market penetration of all-vanadium redox flow batteries is less than 1%. However, in the next few years, all-vanadium redox flow batteries are expected to usher in an explosion. The market is optimistic that the market penetration rate of all-vanadium redox flow batteries will reach 20% by 2025 and 30% by 2030.
Scale growth is bound to bring cost reductions. When cost is no longer a problem, then all-vanadium redox flow batteries may become one of the mainstream routes in the energy storage market.