Key Materials for Vanadium Batteries
Key Materials for Vanadium Batteries
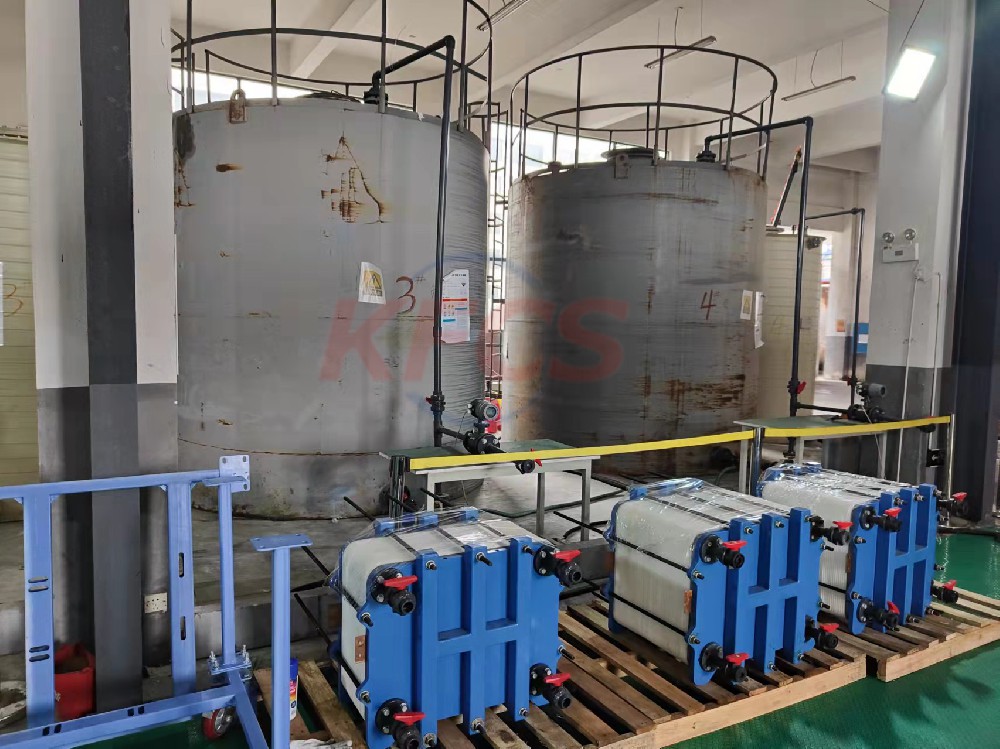
1. Vanadium battery electrolyte All vanadium Initially, the electrolyte was prepared by directly dissolving VOSO4 in H2SO4, but due to the high price of VOSO4, people began to turn their attention to other vanadium compounds such as V2O5, NH4VO3, etc. At present, there are two main methods for preparing electrolyte: mixed heating preparation method and electrolysis method. Among them, the mixed heating method is suitable for preparing 1mol/L electrolyte, and the electrolysis method can prepare 3~5mol/L electrolyte.
2. Vanadium battery separator
The separator of vanadium battery must suppress the cross-mixing of vanadium ions of different valence states in the positive and negative electrolytes, without hindering the passage of hydrogen ions through the separator to transfer charges. This requires the selection of an ion-exchange membrane with good electrical conductivity and good selective permeability, preferably a cation-exchange membrane that allows hydrogen ions to pass through. Battery separators are generally dominated by cation exchange membranes, and Nafion membranes (Dupont) are also used, but the latter are more expensive. One of the ways to improve the efficiency of vanadium batteries is to treat the cation exchange membrane to improve hydrophilicity, selective permeability and prolong service life. The perfluorosulfonic acid type ion exchange membrane was first successfully developed by DuPont, and it is the trademark of Nafion. It is an ion exchange membrane with the best performance at present.
3. Vanadium battery electrode materials
In order to achieve large-capacity energy storage in an all-vanadium redox flow battery, several single cells must be connected in series or in parallel. In this way, except for the terminal electrodes, basically all electrodes are required to be made into dual-polarized electrodes. Due to the strong oxidizing property of V02+ and the strong acidity of sulfuric acid, the electrode material of vanadium battery must have the characteristics of resistance to strong oxidation and strong acidity, low resistance, good electrical conductivity, high mechanical strength, and good electrochemical activity. Vanadium battery electrode materials are mainly divided into three categories: metals, such as Pb, Ti, etc.; carbons, such as graphite, carbon cloth, carbon felt, etc.; composite materials, such as conductive polymers, polymer composites, etc.