Vanadium Redox Battery (VRB) Manufacturer
All Vanadium Redox Flow Battery (VRFB) Vanadium Redox Battery (VRB) Vanadium Flow Battery Manufacturer
Product Description
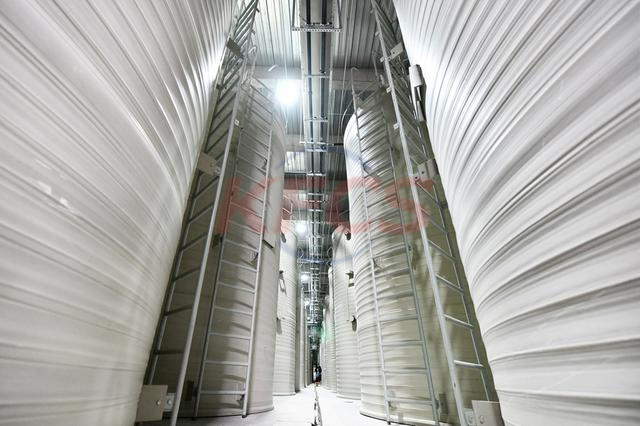
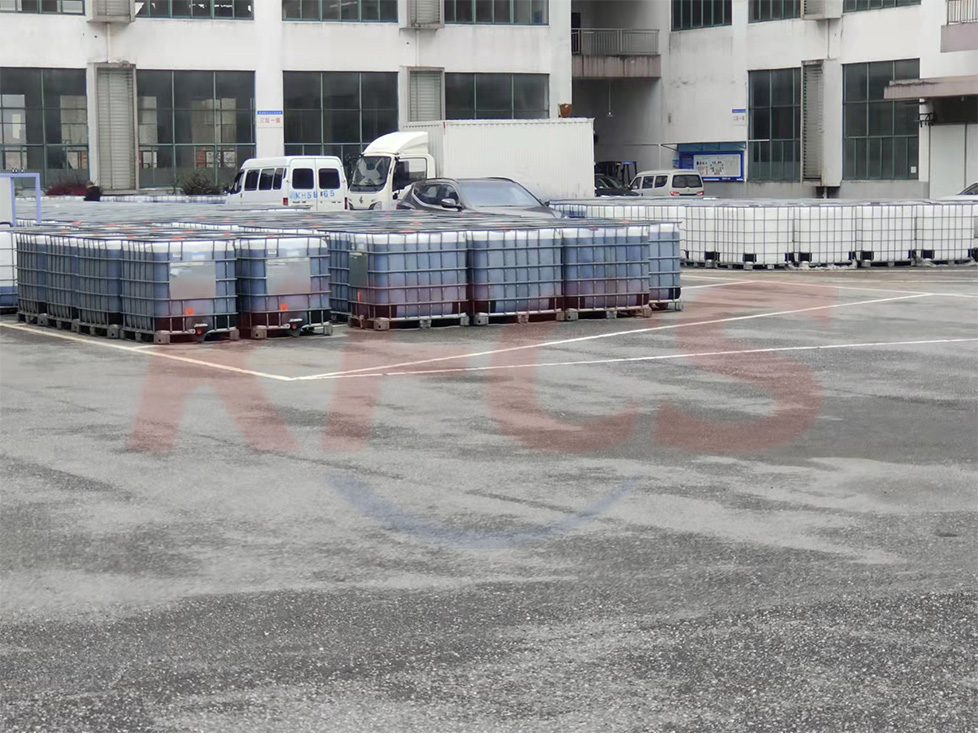
We produce various RFB systems on the market. A vanadium redox flow battery (VRB) that uses vanadium electrolyte on both sides. Such setup gives the advantage of avoiding contamination since the electrolytes are of the same nature, made dominantly from vanadium sulfate and sulfuric acid solution. In the charged state, the positive electrode contains V(5+) ions, while the negative side hosts V(2+). During discharging, the V(5+) is converted into V(4+), V(2+) is converted into V(3+) plus electric power is yielded (see Fig 1). An eventual migration of ions through separator does not cause any damage of system. There are also other RFB systems, which can be realized within the redox potential window of Hydrogen and Oxygen evolution.
Advantages
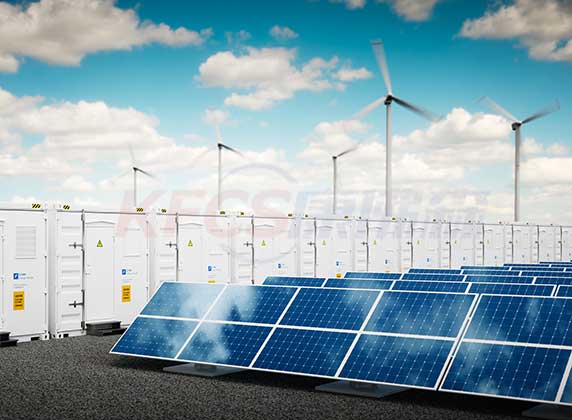
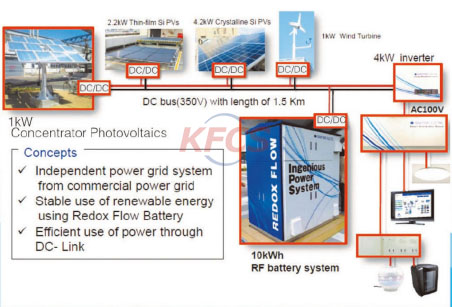
Redox-Flow Batteries (RFB) represent recently the most advanced electro-chemical energy storage system that is commercialized on level tens of kilowatts to megawatts. A flow battery is charged and discharged via reversible electrochemical reduction-oxidation reactions. These reactions take place typically in two liquid electrolytes separated by an ion-exchange membrane. The RFB is scalable system which can be operated in wide range of conditions. It is supposed to be integrated easily into future smart-grids systems and it is advantageous in connection to wind farms. The batteries are further characterized by high longevity in the range of several years, easy maintenance and high overall energy efficiency exceeding 80 %.
Application / Usage
The extremely large capacities possible from vanadium redox batteries make them well suited to use in large power storage applications such as helping to average out the production of highly variable generation sources such as wind or solar power, helping generators cope with large surges in demand or leveling out supply/demand at a transmission constrained region.