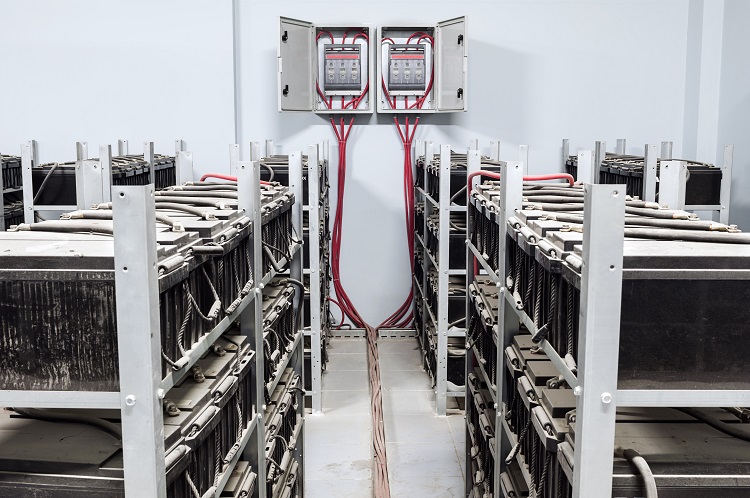
Production method of graphite felt for vanadium battery
The preparation of carbon electrode with high electrochemical activity, high kinetic reversibility, high wettability and high stability is undoubtedly one of the key factors to improve the working efficiency of all vanadium flow battery. At present, many studies have made good experimental progress through the modification of carbon electrode materials, and the experimental results have been continuously applied to commercial production.

Production method of graphite felt for vanadium battery:
The continuous sintering furnace and the continuous activation furnace are connected in series, realizing the transformation from the pre oxygen felt to the graphite felt, and improving the production efficiency and product quality.
The first 2 / 3 sintering furnaces gradually increase in temperature from normal temperature to 1600 ℃, and the second 1 / 3 sintering furnaces gradually decrease in temperature. The first 72% of activation furnaces achieve temperature increase from normal temperature to 960 ℃, and the last 28% of sintering furnaces achieve temperature decrease.
In the production process of the sintering furnace, the ferrocene catalyst can react with carbon sources such as short chain hydrocarbons and amorphous carbon volatilized in the felt under the protection of inert gas to form carbon nanotubes on the surface of the carbon felt, thereby obtaining the modified graphite felt.
Then, the steam or other gases are introduced into the continuous activation furnace to activate the modified graphite felt, that is, high-performance graphite felt products are obtained. During the production process, the maximum sintering temperature range is increased to 1500-1800 ℃, and the maximum activation temperature is adjusted to 800-950 ℃.