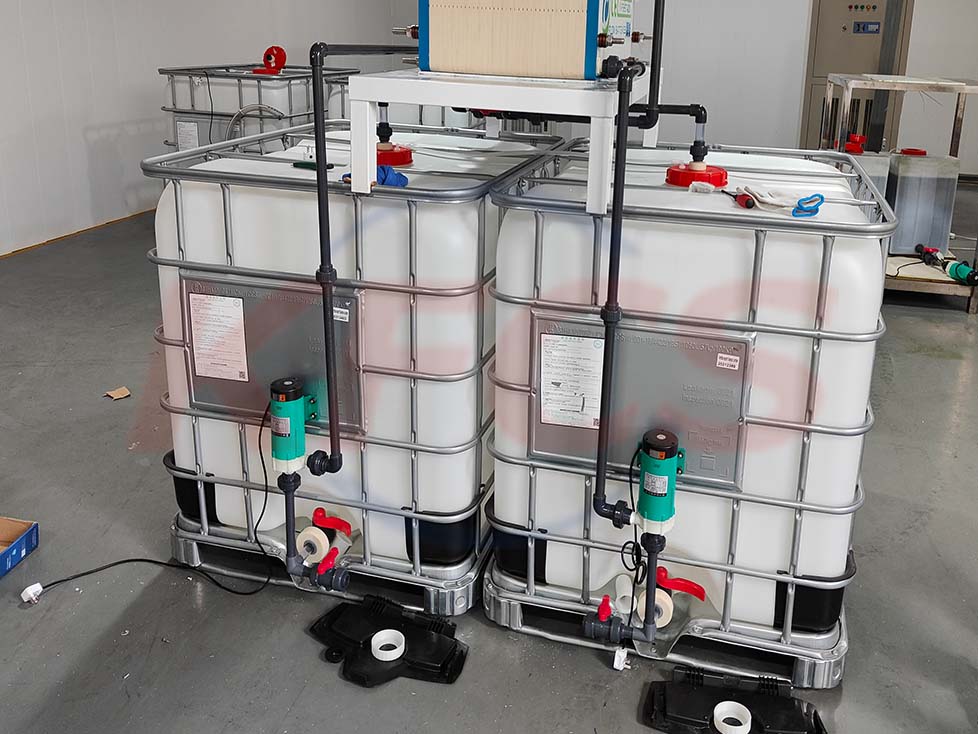
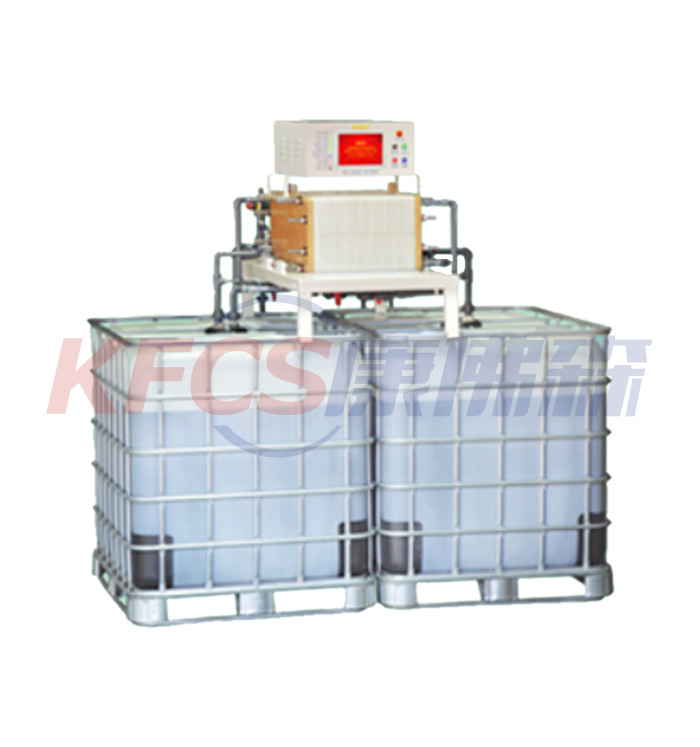
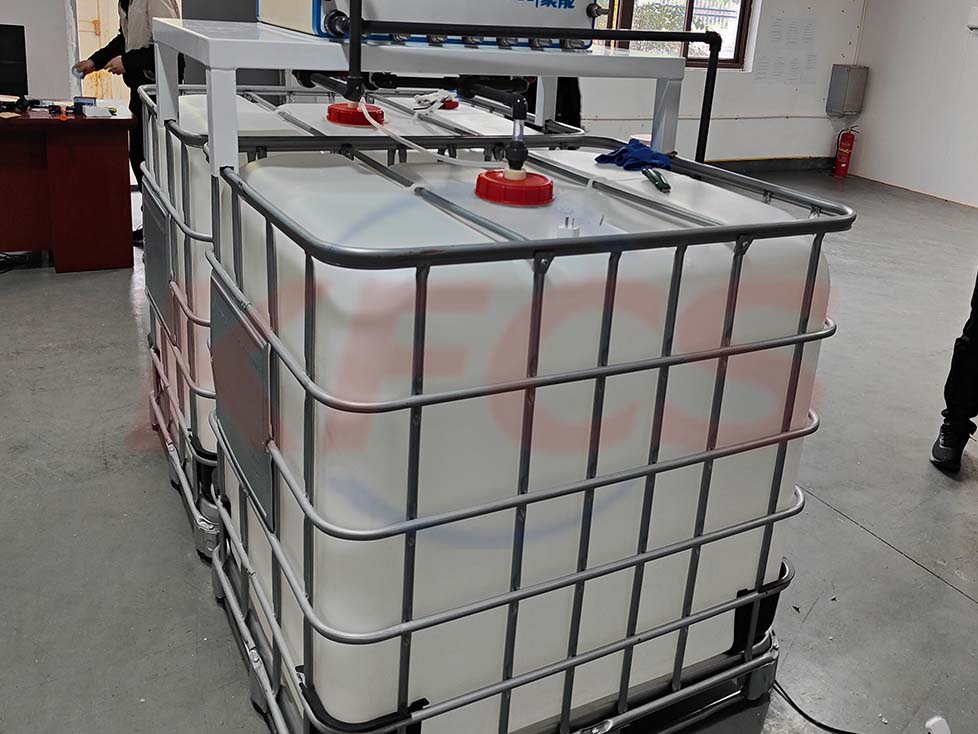
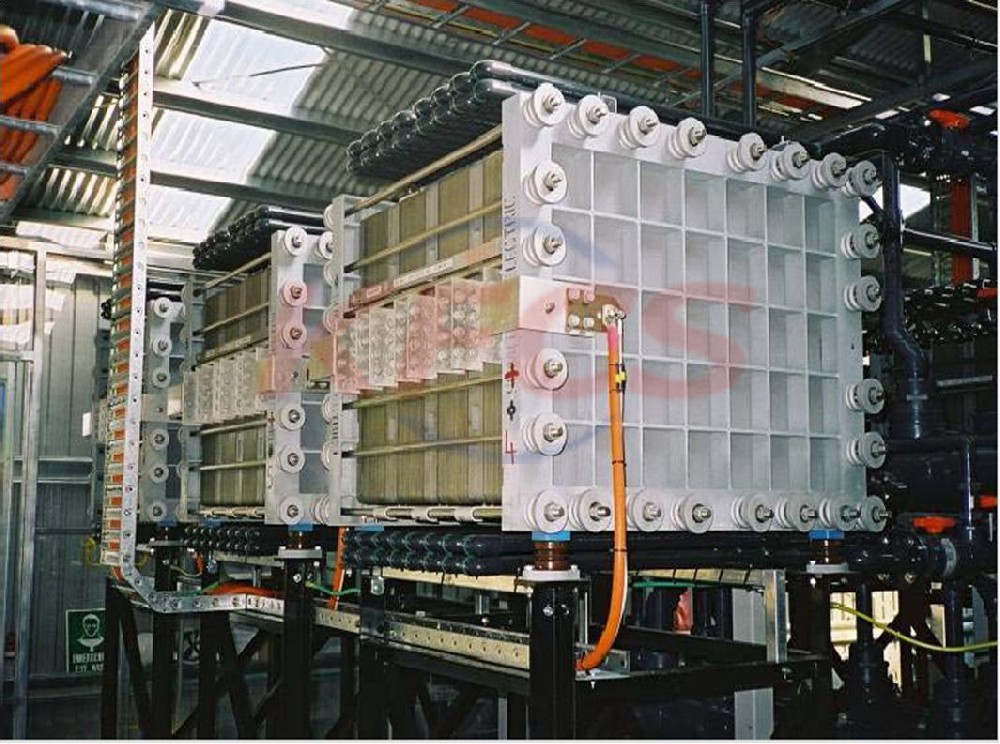
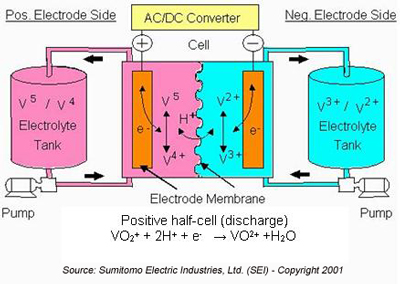
Vanadium redox flow battery (VRFB) systems
Vanadium redox flow battery (VRFB) systems are the most developed among flow batteries because of their active species remaining in solution at all times during charge/discharge cycling, their high reversibility, and their relatively large power output. However, the capital cost of these systems remains far too high for deep market penetration. In order to meet the proposed cost targets, recent investigations have highlighted the use of organic active materials in solid-state organic batteries, in which energy is stored within the cell, mainly in the form of a radical polymer.
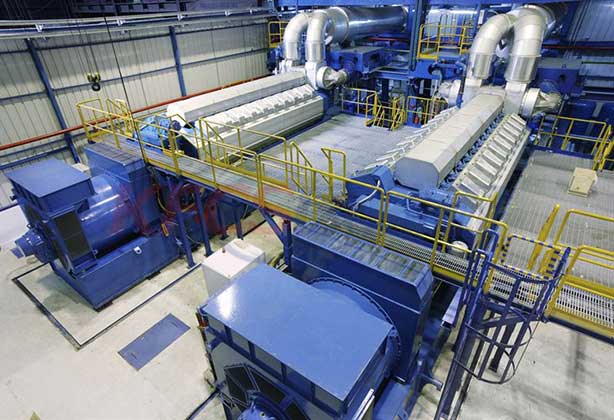
Recently, it has been installed for several purposes. Examples of this technology in use are a 275-kW output balancer on a wind power project in the Tomari Wind Hills, Japan; a 200-kW output leveler on King Island, Australia; a 250-kW, 2-MWh load leveler in Utah, USA; and two wind and solar power projects (5 kW each) installed in Kenya. Additionally, Hokkaido Electric Power Co. Inc. (HEPCO) and Sumitomo Electric Industries (SEI) Ltd. installed 15 MW/60MWh of VRFB at the Minamihayakita Transformer Station in Abira-chou, Hokkaido, Japan—this is one of the world's largest redox flow battery operations in use.