The charging and discharging principle and comparison of advantages and disadvantages of all-vanadium flow battery in energy storage system
The charging and discharging principle and comparison of advantages and disadvantages of all-vanadium flow battery in energy storage system
1. Principle of charging and discharging of all-vanadium redox flow battery
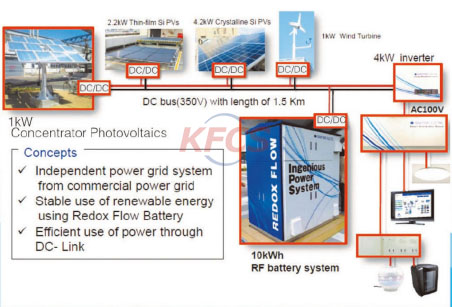
All-vanadium redox flow battery is a kind of redox renewable fuel cell based on metal vanadium. The energy storage system of vanadium battery is stored in the sulfuric acid electrolyte of different valence vanadium ions in the form of chemical energy. Into the battery stack, under the action of mechanical power, it circulates in the closed loop of different liquid storage tanks and half cells, using the proton exchange membrane as the diaphragm of the battery pack, the electrolyte solution flows parallel to the electrode surface and electrochemistry occurs. The reaction, which collects and conducts electrical current through the bipolar plates, allows the chemical energy stored in the solution to be converted into electrical energy. This reversible process enables the vanadium battery to successfully complete the cycle charge and discharge.
2. Key materials for all-vanadium redox flow batteries
1. Electrode material
(1) It has high activity for the chemical reaction of the positive and negative electrodes of the battery, and reduces the spark potential of the electrode reaction;
(2) Excellent electrical conductivity, reducing the ohmic polarization of the battery during charging and discharging;
(3) Better three-dimensional structure, which facilitates the flow of electrolyte and reduces the loss of the circulating pump for transporting electrolyte when the battery is working;
(4) High chemical and electrochemical stability, prolonging the service life of the battery.
2. Ion exchange membrane
(1) High selectivity;
(2) Low film resistance;
(3) Sufficient chemical stability.
3. Electrolyte
3. Comparison of advantages and disadvantages of all-vanadium redox flow batteries
advantage:
(1) The design is flexible. When the output power is constant, if you want to increase the energy storage capacity, you only need to increase the volume of the electrolyte storage tank or increase the electrolyte concentration;
(2) The active material of the vanadium battery exists in the liquid, and the electrolyte ion is only one type of vanadium ion, so there is no phase change common in other batteries during charging and discharging, and the battery has a long service life;
(3) The charging and discharging performance is good, and it can be deeply discharged without damaging the battery;
(4) Low self-discharge, when the system is in shutdown mode, the electrolyte in the storage tank has no self-discharge phenomenon;
(5) The vanadium battery has a large degree of freedom in site selection, and the system can be fully automatic closed operation, pollution-free, simple maintenance, and low operating cost;
(6) The battery system has no potential explosion or fire hazard, and has high safety;
(7) Most of the battery components are cheap carbon materials and engineering plastics, which are rich in material sources and easy to recycle, and do not require precious metals as electrode catalysts;
(8) High energy efficiency, up to 75%-80%, very cost-effective;
(9) The start-up speed is fast. If the stack is full of electrolyte, it can be started within 2 minutes, and it only takes 0.02s to switch the charge-discharge state during operation.
shortcoming:
(1) The volume is relatively large;
(2) Usually suitable for large-capacity storage;
(3) During the actual operation, the monitoring system lacks the means of monitoring leakage.